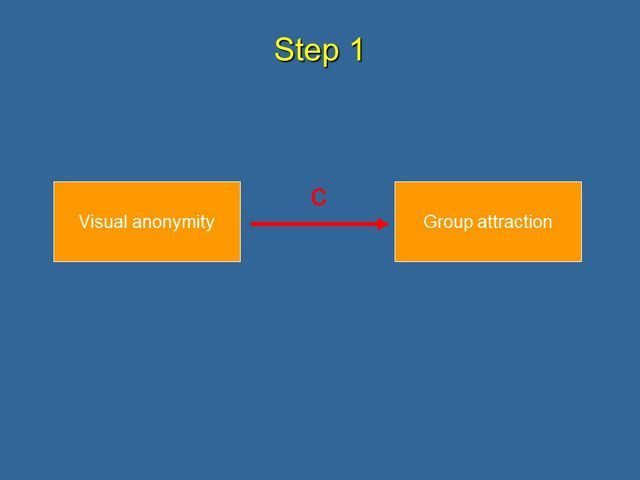
Let's start by decomposing mediation into a number of causal steps as described by Baron & Kenny (1986). We'll use our mediation model for the effects of Visual Anonymity on Group Attraction, mediated by Self-Categorization.
The fist step is to show that the initial variable affects the outcome. In our model, we need to show that visual anonymity affects group attraction. Let's call this path c.
In order to measure this effect (path c), we need to do a simple linear regression of the criterion variable (Group Attraction) on the predictor variable (Visual Anonymity). If there is a significant effect, we know that an effect is present, and we can proceed in, Step 2, to test whether the effect is mediated.
NEXT: 8. Causal Steps to Establish Mediation: Step 2
Statistics Training: Introduction to Path Analysis
- 9. Causal Steps to Establish Mediation: Steps 3 & 4
- 8. Causal Steps to Establish Mediation: Step 2
- 7. Causal Steps to Establish Mediation: Step 1
- 6. Mediation Analysis: Procedures and Tests
- 5. Example of a Basic Test of Mediation
- 4. Example of the Difference between Moderation and Mediation
- 3. Moderation and Mediation Explained
- 2. A Quick Review of Regression
- 13. Sobel's Test of Significant Mediation
- 12. Testing for Significant Mediation
- 11. An Example of a Mediator Acting as a Suppressor
- 10. Barron and Kenny (1986) Criteria for Mediation
- 1. What is Path Analysis?