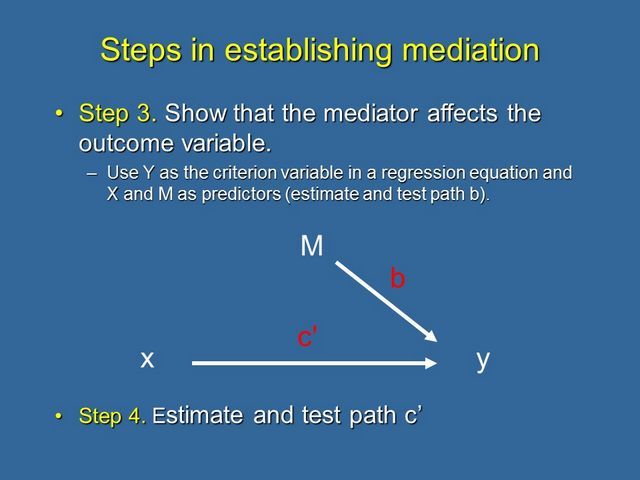
Steps 3 and 4 are conducted simultaneously using multiple regression. Step 3 consists of regressing the outcome variable y onto both the mediator, m, and the predictor, x to provide an estimate of path b.
Note: it is not sufficient just to correlate the mediator with the outcome; the mediator and the outcome may be correlated because they are both caused by the initial variable X. Thus, the initial variable must be controlled in establishing the effect of the mediator on the outcome.
Step 4 is simply the estimate c' of the effect of x on y, controlling for the effect of m, which is output in the same multiple regression. If c' is zero, complete mediation of the effect has occurred. If c' is not zero, then partial mediation has occurred.
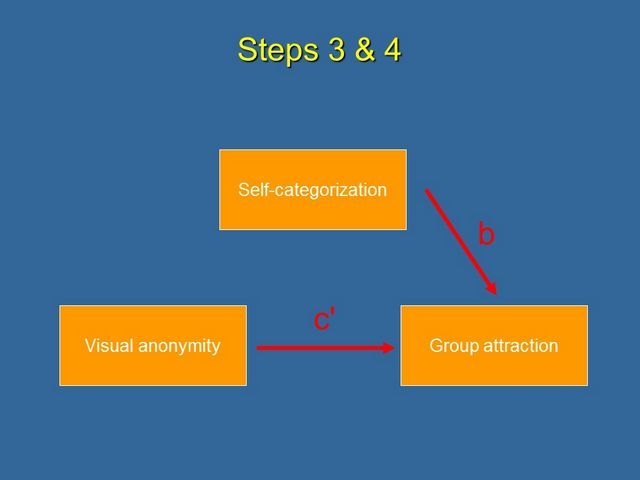
In our example we use multiple regression to regress group attraction on to both visual anonymity and self-categorization (Steps 3 and 4). From this we obtain the estimate of the effect of Self-categorization on group attraction, controlling for visual anonymity (path b), and the effect of visual anonymity on group attraction, controlling for Self-categorization (path c').
If the estimate of path c' is not zero, then the effect of visual anonymity on group attraction is only partially mediated by self-categorization.
NEXT: 10. Barron and Kenny's (1986) Criteria for Mediation
Statistics Training: Introduction to Path Analysis
- 9. Causal Steps to Establish Mediation: Steps 3 & 4
- 8. Causal Steps to Establish Mediation: Step 2
- 7. Causal Steps to Establish Mediation: Step 1
- 6. Mediation Analysis: Procedures and Tests
- 5. Example of a Basic Test of Mediation
- 4. Example of the Difference between Moderation and Mediation
- 3. Moderation and Mediation Explained
- 2. A Quick Review of Regression
- 13. Sobel's Test of Significant Mediation
- 12. Testing for Significant Mediation
- 11. An Example of a Mediator Acting as a Suppressor
- 10. Barron and Kenny (1986) Criteria for Mediation
- 1. What is Path Analysis?