Path Analysis Made Easy.
Take my Statistics Course
An Introduction to Path Analysis: Theory and Practice.
In this introductory module I introduce the concept of mediation and differentiate it from moderation. I’ll describe and illustrate what a simple case of mediation looks like with some real world data. When you're comfortable with the idea of mediation, I'll show you some different techniques to test for significant mediated effects in your data and discuss the best one to use.
In the second module I'll introduce the main concepts you need to understand Path Analysis (or Causal Modeling as it is otherwise known) and show you how to do various kinds of modelling using the AMOS program, which is available online. I’ll be showing you how to construct and test some simple models using techniques you can apply to your own data.
This course is useful for research who want to model their own data. However, a second purpose of this course is to provide you with the knowledge you need to interpret descriptions of causal models that you may read about. Causal modeling is becoming increasingly popular, especially in social and clinical fields, and it is important to be able to interpret and evaluate a model you may come across in your own research or in a journal article which an editor has asked you to review.
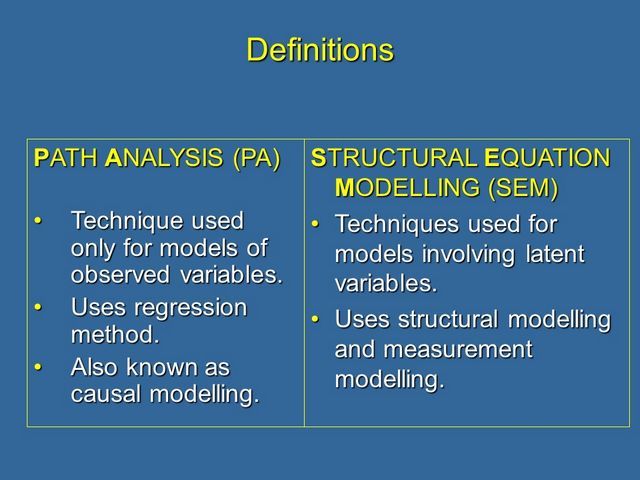
1. What is Path Analysis?
Path analysis and structural equation modeling are techniques to assess the direct causal contribution of one variable to another in a non experimental situation. They are therefore particularly useful in field studies, and have become increasingly popular as modern psychology draws from real problems and non-laboratory research methods. However, as…
10. Barron and Kenny (1986) Criteria for Mediation
This slide summarizes Barron & Kenny's (1986) causal steps for establishing mediation, which we have just discussed. However, do all of the steps have to be met for there to be mediation? Certainly, Step 4 does not have to be met unless the expectation is for complete mediation. Moreover, Step…
11. An Example of a Mediator Acting as a Suppressor
Statistics Training: Introduction to Path Analysis
12. Testing for Significant Mediation
Statistics Training: Introduction to Path Analysis
13. Sobel's Test of Significant Mediation
Statistics Training: Introduction to Path Analysis
2. A Quick Review of Regression
What is Simple Regression? What is Multiple Regression? In simple regression a single dependent or criterion variable is related to a single independent variable or predictor variable. Multiple regression is an extension of simple regression in which the criterion is regressed against several potential predictors. For example, a simple…
3. Moderation and Mediation Explained
Path models are built up from basic models of moderation and/or mediation. It is common in psychology for the terms moderator and mediator to be used interchangeably. However, they are conceptually different. “In general terms, a moderator is a qualitative (e.g., sex, race class) or quantitative (e.g., level of reward)…
4. Example of the Difference between Moderation and Mediation
This example illustrates the importance of clearly specifying your theory in terms of moderators and mediators. It's taken from an advisory session with a PhD student who approached me to discuss how to test her theory. Her project was looking at the link between language deficit and self-esteem in young adults. Her hypothesis…
5. Example of a Basic Test of Mediation
The simplest mediation analysis involves a single independent variable, a dependent variable, and a hypothesized mediator. The unmediated model is represented by the direct effect of x on y, quantified as c. However, the effect of X on Y may be mediated by a process, or mediating variable M. Complete…
6. Mediation Analysis: Procedures and Tests
So how do we go about doing a mediation analysis? In the next four posts I'll take you through the main approaches to testing for a significant mediation effect. We'll first look at the Causal Steps approach, made famous by Baron & Kenny (1986). Then we'll look at several modern…
7. Causal Steps to Establish Mediation: Step 1
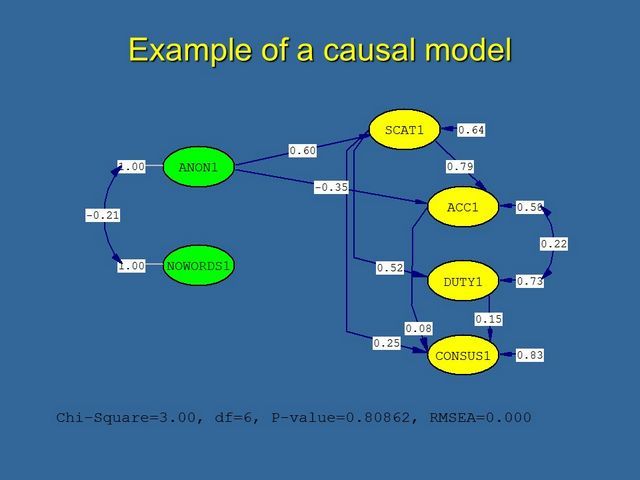
Let's start by decomposing mediation into a number of causal steps as described by Baron & Kenny (1986). We'll use our mediation model for the effects of Visual Anonymity on Group Attraction, mediated by Self-Categorization. The fist step is to show that the initial variable affects the outcome. In our…
8. Causal Steps to Establish Mediation: Step 2
In the second step, we need to show that the initial, or predictor, variable affects the mediator. So we perform another simple linear regression using the mediator as if it were the outcome variable and regressing it on the predictor, which gives us an estimate of path a. In our…
9. Causal Steps to Establish Mediation: Steps 3 & 4
Steps 3 and 4 are conducted simultaneously using multiple regression. Step 3 consists of regressing the outcome variable y onto both the mediator, m, and the predictor, x to provide an estimate of path b. Note: it is not sufficient just to correlate the mediator with the outcome; the mediator…